When it comes to IoT, the ESP32 is a chip that packs a powerful punch. The ESP32 is a follow-up to the ESP8266. This low-cost system on a chip (SoC) series was created by Espressif Systems. Based on its value for the price, small size, and relatively low power consumption, the ESP32 is well-suited to a number of different IoT applications.
In this article, I’ll break down the ESP32’s technical specifications and describe some of the different modules available.
What is ESP32?
ESP32 is a chip that provides Wi-Fi and (in some models) Bluetooth connectivity for embedded devices – in other words, for IoT devices. While ESP32 is technically just the chip, the modules and development boards that contain this chip are often also referred to as “ESP32” by the manufacturer.
The original ESP32 chip had a single core Tensilica Xtensa LX6 microprocessor. The processor had a clock rate of over 240 MHz, which made for a relatively high data processing speed.
More recently, new models were added, including the ESP32-C and -S series, which include both single and dual core variations. These two series also rely on a Risc-V CPU model instead of Xtensa. Risc-V is similar to the ARM architecture, which is well-supported and well-known, but Risc-V is open source and easy to use. Specifically, Risc-V and ARM have good support from GNU compilers, while the Xtensa needed extra support and development to work with the compilers.
The newer models are available with combined Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, or just Wi-Fi connectivity. There are several different chip models available, including:
- ESP32-D0WDQ6 (and ESP32D0WD)
- ESP32-D2WD
- ESP32-S0WD
- System in package (SiP) – ESP32-PICO-D4
- ESP32 S series
- ESP32-C series
- ESP32-H series
The ESP32 is most commonly used for mobile devices, wearable tech, and IoT applications, such as Nabto Edge. Moreover, since Mongoose OS introduced an ESP32 IoT Starter Kit, the ESP32 has gained a reputation as the ultimate chip for hobbyists and IoT developers. It’s suitable for commercial IoT, and its capabilities and resources have grown impressively over the past four years.
ESP32 features and specifications
Here’s a high-level summary of the features and specifications of the ESP32:
ESP-32 | DESCRIPTION |
Core | 2 |
Architecture | 32 bits |
Clock | Tensilica Xtensa LX106 160-240MHz |
WiFi | IEEE802.11 b/g/n |
Bluetooth | Yes - classic & BLE |
RAM | 520KB |
Flash | External QSPI - 16MB |
GPIO | 22 |
DAC | 2 |
ADC | 18 |
Interfaces | SPI-I2C-UART-I2S-CAN |
And here’s a more detailed summary:
- Processors – The ESP32 uses a Tensilica Xtensa 32-bit LX6 microprocessor. This typically relies on a dual core architecture, with the exception of one module, the ESP32-S0WD, which uses a single-core system. The clock frequency reaches up to 240MHz and it performs up to 600 DMIPS (Dhrystone millions of instructions per second). Moreover, its low power consumption allows for analog to digital conversions as well as computation and level thresholds, even while the chip is in deep sleep mode.
- Wireless connectivity – The ESP32 enables connectivity to integrated Wi-Fi through the 802.11 b/g/n/e/i/. Moreover, Bluetooth connectivity is made possible with the v4.2 BR/EDR, and the series also features Bluetooth low energy (BLE).
- Memory – Internal memory for the ESP32 is as follows. ROM: 448 KB (for booting/core functions), SRAM: 520 KB (for data/instructions), RTC fast SRAM: 8 KB (for data storage/main CPU during boot from sleep mode), RTC slow SRAM: 8 KB (for co-processor access during sleep mode), and eFuse: 1 KiBit (256 bits used for the system (MAC address and chip configuration) and 768 bits reserved for customer applications). Moreover, some of the ESP32 chips, including the ESP32-D2WD and ESP32-PICO-D4, have internally connected flash. See the respective internal flash memory for each chip in the ESP32 Chips section.
- External flash and SRAM – ESP32 supports up to four 16 MB external QSPI flashes and SRAMs with hardware encryption based on AES to protect developers’ programs and data. It accesses the external QSPI flash and SRAM through high-speed caches.
- Security – The ESP32 supports all IEEE 802.11 standard security features, including WFA, WPA/WPA2 and WAPI. Moreover, ESP32 has a secure boot and flash encryption.
ESP32 functions
ESP32 has many applications when it comes to IoT. Here are just some of the IoT functions the chip is used for:
- Networking: The module’s Wi-Fi antenna and dual core enables embedded devices to connect to routers and transmit data.
- Data processing: Includes processing basic inputs from analog and digital sensors to far more complex calculations with an RTOS or non-OS software development kit (SDK). A non-OS SDK refers to one that is designed to run directly on the chip without a full operating system supporting it.
- P2P connectivity: Creates direct communication between different ESPs and other devices using IoT P2P connectivity.
- Web server: Provides access to pages written in HTML or development languages.
ESP32 Applications
The ESP32 modules are commonly found in the following IoT devices:
- Smart industrial devices, including programmable logic controllers (PLCs)
- Smart medical devices, including wearable health monitors
- Smart energy devices, including HVAC and thermostats
- Smart security devices, including surveillance cameras and smart locks
Chip versus modules versus development boards
The ESP32 is just the name of the chip. Device manufacturers and developers have three different format choices, and the decision of which one to go with will depend on their individual circumstances:
- ESP32 chip: This is the bare-bones chip that is manufactured by Espressif. It comes unshielded, meaning there’s no protective casing, and it can’t be attached to a module or board without soldering. Therefore, most device manufacturers do not purchase just the chip, as this will add an additional layer of complexity to the production process.
- ESP32 modules: These are surface mountable modules that contain the chip. The modules are essentially small electrical components that can be attached to a circuit board. The benefit here is that you can easily mount these modules onto an MCU board. The chip is also usually shielded and pre-approved by the FCC, which means device manufacturers do not need to worry about adding additional steps to the production process to achieve FCC compliance regarding Wi-Fi shielding.
- ESP32 development boards: These are IoT MCU development boards that have the modules containing the ESP32 chip preinstalled. They are used by hobbyists, device manufacturers and developers to test and prototype IoT devices before entering mass production. There is a wide variety of makes and models of ESP32 development boards, produced by different manufacturers. Here are some important specs to consider when choosing a suitable IoT ESP32 development board:
- GPIO pins
- ADC pins
- Wi-Fi antennas
- LEDs
- Shielding*
- Flash memory
*Many international markets require shielded Wi-Fi devices, as Wi-Fi produces a lot of radio frequency interference (RFI), and shielding minimizes this interference. This should, therefore, be a key consideration for all developers and embedded device manufacturers.
Manufacturers of ESP32 modules and boards
ESP32 Chips
Espressif Systems is the manufacturer of the ESP32 chip. The chip is available in various sizes, including 7 mm x 7 mm, 6 x 6, 5 x 5, and even 4 x 4 QFN packages. Here are the current models available:
Model | Package size | Embedded flash memory (MB) | Processor cores |
ESP32-D0WDQ6 | 6 mm x 6 mm | 0 | 2 |
ESP32-D0WD | 5 mm x 5 mm | 0 | 2 |
ESP32-D2WD | 5 mm x 5 mm | 2 | 2 |
ESP32-U4WDH | 5 mm x 5 mm | 4 | 1 |
ESP32-S0WD | 5 mm x 5 mm | 0 | 1 |
ESP32-S2 | 7mm x 7 mm | N/A | 1 |
ESP32-S2F | 7mm x 7 mm | 2-4 | 1 |
ESP32-S3 | 7mm x 7 mm | 0-8 | 2 |
ESP32-SE-PICO-1 | 7mm x 7 mm | 8 | 1 |
ESP8684 | 4 mm x 4 mm | 2-4 | 1 |
ESP32-C3 | 5 mm x 5 mm | 0-4 | 1 |
ESP8685 | 4 mm x 4 mm | 2-4 | 1 |
ESP32-C6 | 5 mm x 5 mm | 0-4 | 1 |
ESP32-H2 | 4 mm x 4 mm | 2-4 | 1 |
ESP32 modules
● Espressif
There are too many modules to mention all of them here, but here are some of the top modules that use the Espressif Systems ESP32 chip:
Model | Dimensions | PINS | Antennae | Flash |
ESP-WROOM-32 | 18 x 25.5 x 2.8 | 38 | PCB trace | 4 MB |
ESP-WROOM-32D | 18 x 25.5 x 3.1 | 38 | PCB trace | 4 MB |
ESP-WROOM-32U | 18 x 19.2 x 3.2 | 38 | U.FL Socket | 4 MB |
ESP-WROVER | 18 x 31.4 x 3.3 | 38 | PCB trace | 4 MB |
ESP-WROVER-I | 18 x 31.4 x 3.3 | 38 | U.FL Socket, PCB | 4 MB |
ESP-WROVER-B | 18 x 31.4 x 3.3 | 38 | PCB trace | 4 MB |
ESP-WROVER-IB | 18 x 31.4 x 3.3 | 38 | U.FL Socket, PCB | 4 MB |
ESP32-S2-WROOM | 18 × 31 × 3 | 37 | U.FL Socket, PCB | 4 MB |
ESP32-S3-WROOM-1 | 25.5 x 18 x 3.1 | 41 | U.FL Socket, PCB | 4-16 MB |
● Ai-Thinker
Current Ai-Thinker ESP32 modules are the following:
Model | Dimensions | PINS | Antennae | Flash |
ESP32-S | 18 x 25.5 x 2 | 38 | PCB trace | 4 MB |
ESP32-A1S | 18 x 25.5 x 2 | 38 | U.FL Socket, PCB trace | 4 MB |
Other manufacturers of ESP32 modules include:
ESP32 development boards/dev kits
● Espressif
The current Espressif ESP32 development boards include:
Model | Onboard module | Firmware | USB | Flash |
ESP32-DevKitC | ESP-WROOM-03 | Espressif Non-OS SDK, using Lua scripting language | USB to serial interface | 4 MB flash |
ESP-WROVER-KIT | ESP-WROOM-32 or ESP32-WROVER | Espressif Non-OS SDK, using Lua scripting language | USB to serial interface | 4 MB flash + 8 MB PSRAM |
ESP32-PICO-KIT | ESP32-PICO-D4 | Espressif Non-OS SDK, using Lua scripting language | USB to serial interface | 4 MB flash |
ESP32-S2-Kaluga-1 | ESP32-S2-WROVER | Espressif Non-OS SDK, using Lua scripting language | USB to serial interface | 4 MB flash |
● Ai-Thinker
The AI-Thinker development boards include:
Model | Onboard module | Firmware | GPIO & ADC Pins | USB | Flash |
NodeMCU-32S | ESP-WROOM-32 | Lua, AT commands, MicroPython, Arduino | 38 | USB port for power input | 32 MB |
ESP32-CAM | ESP32-CAM | Embedded Lwip and FreeRTOS | 9 | USB port for power input | 32 MB |
● Adafruit
The Adafruit ESP32 development boards include:
Model | Onboard module | Firmware | GPIO & ADC Pins | USB | Flash |
HUZZAH32 | ESP-WROOM-32 | ESP-IDF and Arduino IDE software | 24 | USB to serial interface | 4 MB |
● Wemos
The Wemos ESP32 development boards include:
Model | Onboard module | Firmware | GPIO & ADC Pins | USB | Flash |
LOLIN D32 | ESP-WROOM-32 | Compatible with Arduino, MicroPython | 19 | USB to serial interface | 4 MB |
LOLIN D32 PRO | ESP-WROOM-32 | Compatible with Arduino, MicroPython | 19 | USB to serial interface | 16 MB/4 MB Flash 4 MB PSRAM |
● Arducam
The current Arducam ESP32 development board is:
Model | Onboard module | Firmware | GPIO & ADC Pins | USB | Flash |
ESP32 UNO | ESP-32S | Compatible with Arduino IDE | 23 | Built in micro USB | 32Mbit Flash, 8MByte PSRAM |
What SDKs are used for ESP32s?
A wide range of SDKs are now available. Espressif provides one official SDK for use with either the ESP32, ESP32-2, or the ESP8266. This is the FreeRTOS-based SDK. FreeRTOS is the real-time operating system offered by Amazon, so the SDK is specifically designed for use with that system.
Aside from the Espressif options, there are plenty of commercial and open-source SDKs on the market, including:
- ESP Arduino Core – C++ based firmware
- ESP-SDK-Tools – Open integrated SDK for ESP8266
- Espruino – Javascript SDK and firmware
- Micropython – Python for embedded devices
- Moddable SDK – Javascript SDK
- Mongoose OS – C or Javascript open-source OS
- NodeMCU – Open-source Lua based firmware, similar to Node.js
- uLisp – Lisp-based framework
- Zerynth – Python framework for IoT
Which is the best ESP32 module or development board for IoT?
As the above comparisons show, there are a lot of options available with ESP32 IoT boards and modules. To help you with your decision making, we’ve summarized some of the most popular below.
Popular ESP32 modules
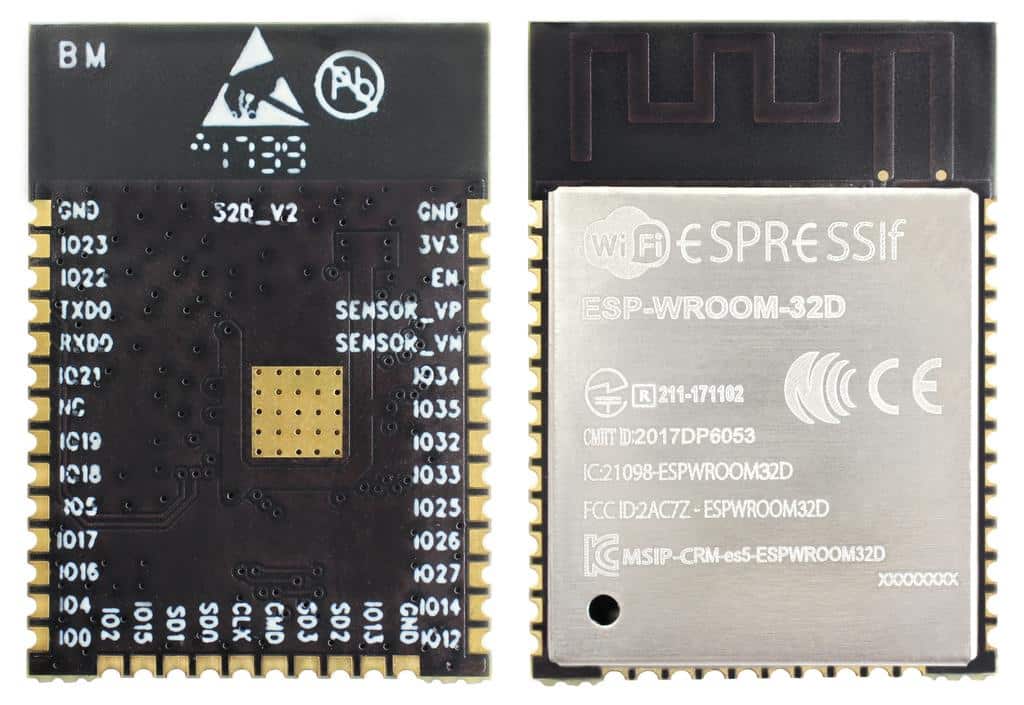

ESP32-WROOM-32D
This extremely popular ESP32 module integrates with the ESP32-D0WD. The main reason that the ESP32-WROOM-32D is such a popular module is its adaptability. It can target a variety of applications, including anything from lower-powered sensor networks to voice encoding and music streaming.
The ESP32-WROOM-32D is often confused with the ESP32-WROOM 32U. Though they are very similar modules, ESP32-WROOM-32U is different from ESP32-WROOM-32D in that the ESP32-WROOM-32U integrates a U.FL connector.
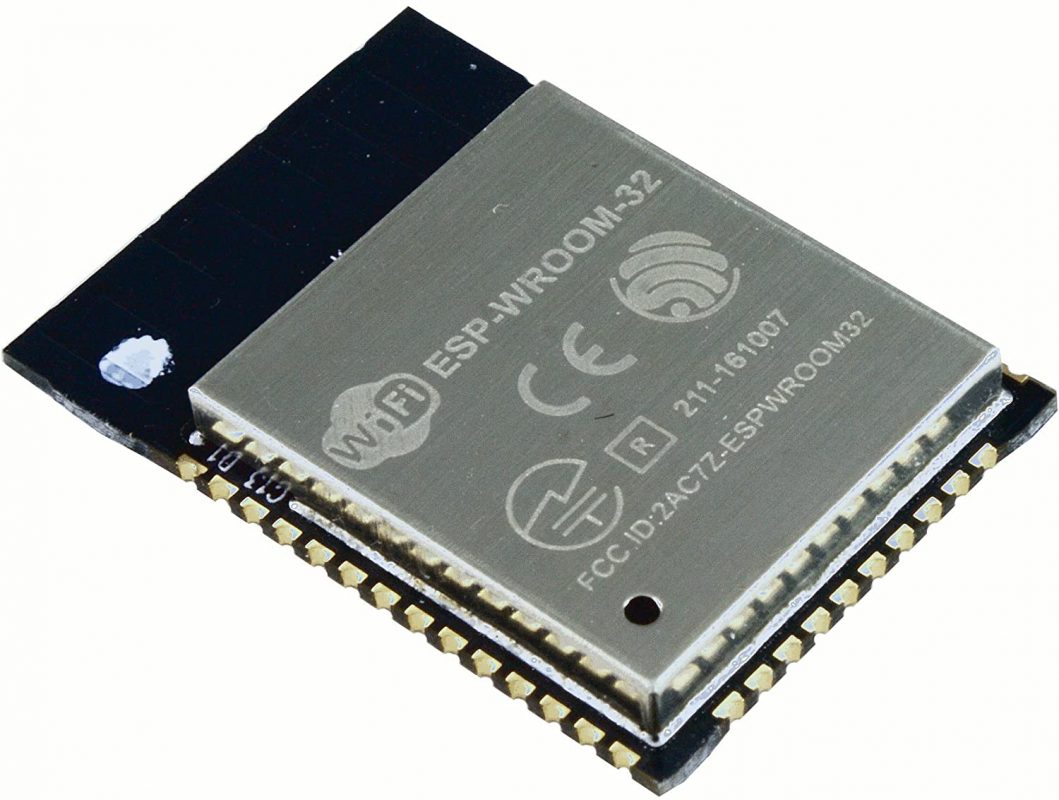

ESP32-WROOM-32
The ESP32-WROOM-32 is the original ESP32 module developed by Espressif. ESP32-WROOM-32 is a powerful, generic Wi-Fi+BT+BLE MCU module. At the core of this module is the ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip. The embedded chip is designed to be scalable and adaptive.
While there’s no denying the ESP32-WROOM-32 is a great module, it is not recommended for new designs. Manufacturers will sometimes say a module is not for new designs if it is nearing the end of its production life or if it is expected to become obsolete for some reason.
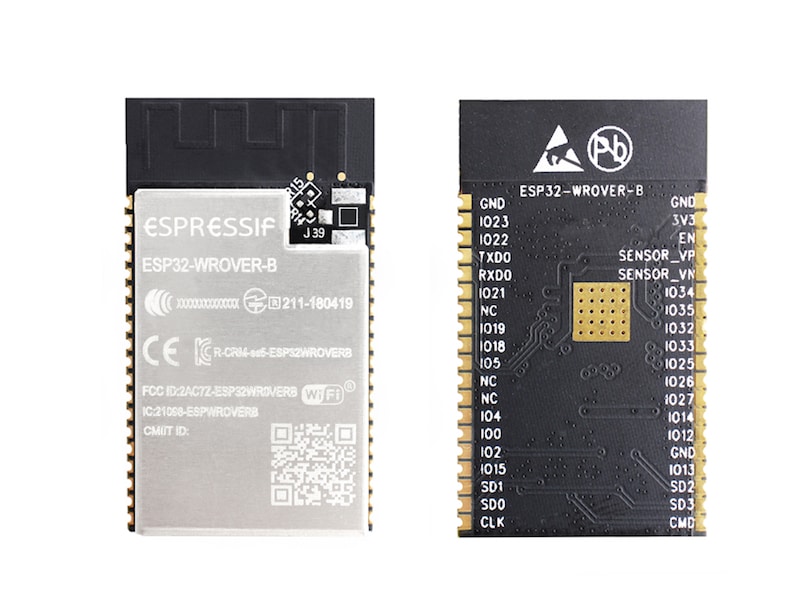

ESP32-WROOVER
The ESP32-WROOVER module has two versions: one with a PCB antenna, the other with an IPEX antenna. You can find the ordering information for both versions here. Like the ESPWROOM32, the chip at the core of this module is the ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip.
This ESP32 module features two CPU cores that can be individually controlled. Moreover, the CPU clock frequency is adjustable from 80 MHz to 240 MHz. The user may also power off the CPU and use the low-power co-processor to continuously monitor for changes or crossing thresholds.
Popular ESP32 development boards
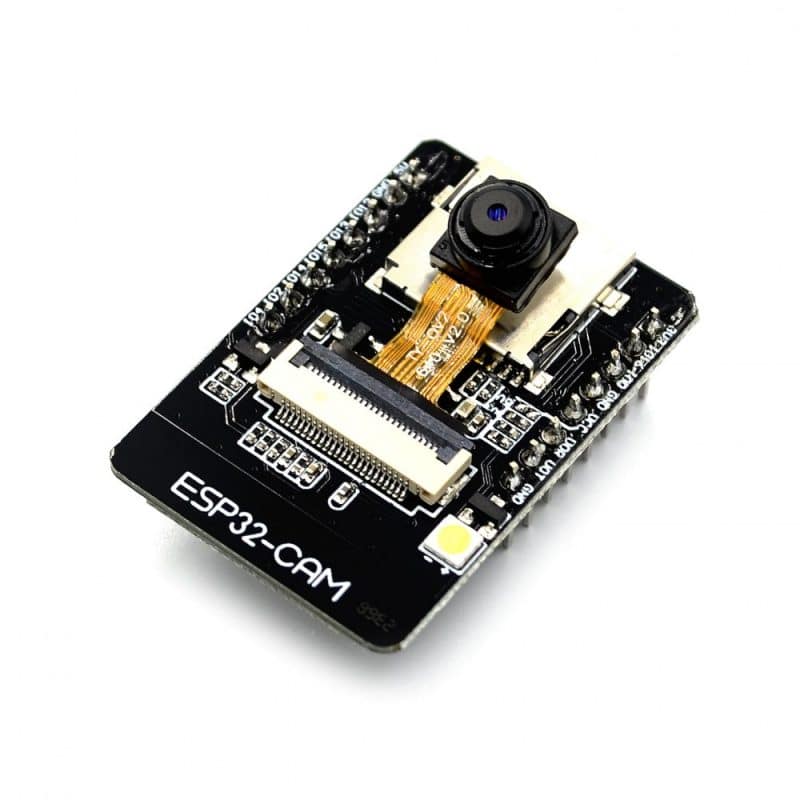

ESP32 CAM
The ESP32 CAM is a little different from the other development boards on this list. This fully-developed microcontroller also has an integrated camera and micro SD card socket.
The ESP32-CAM is based on the ESP32-S module, so it shares the same specifications. This includes UART, SPI, I2C and PWM interfaces, Wi-Fi image upload, clock speeds of up to 160 MHz, and nine GPIO ports.
It also includes an OV2640 module – which has a 2 Megapixel sensor – and also supports OV7670 cameras, too.
As there are many components on the bottom, it may be easier to avoid a solderless breadboard when experimenting with the ESP32-CAM. Furthermore, the use of jumpers with female Dupont connectors is recommended.
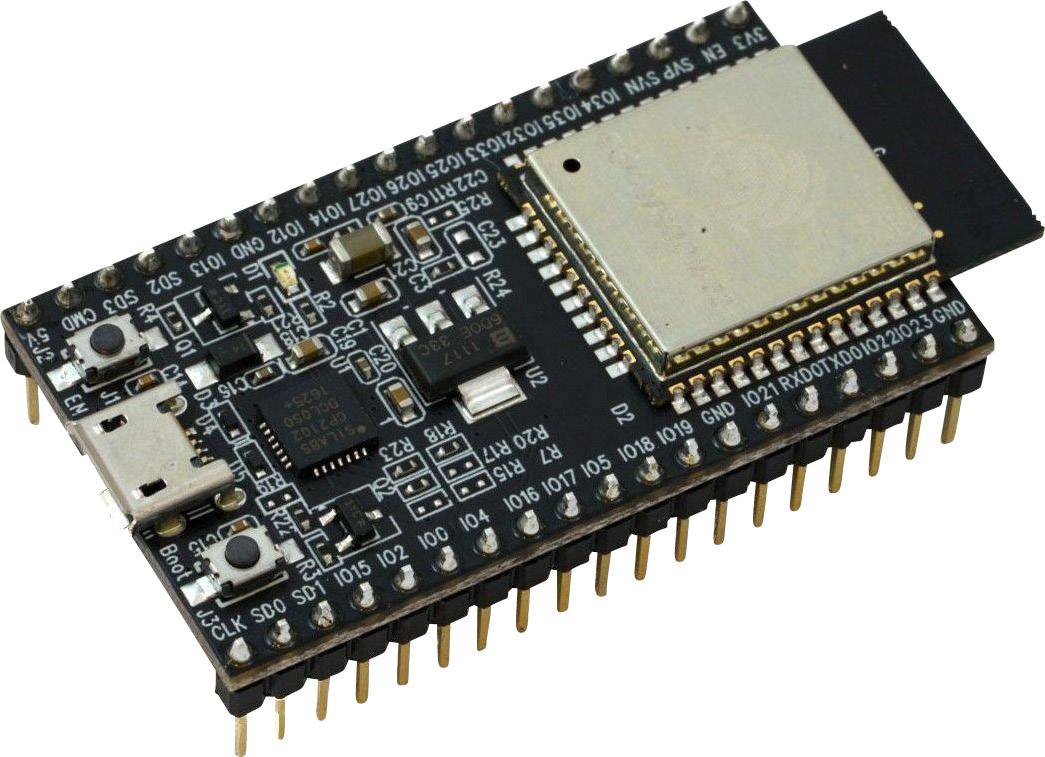
ESP32-DevKitC
The ESP-DevKitC is a relatively small development board from Espressif. The I/O pins are broken out to the pin headers on both sides for easy interfacing. Developers can connect peripherals with jumper wires or mount the ESP32-DevKitC V4 on a breadboard.
A key advantage of this development board is not just its small size, but also its low power usage.
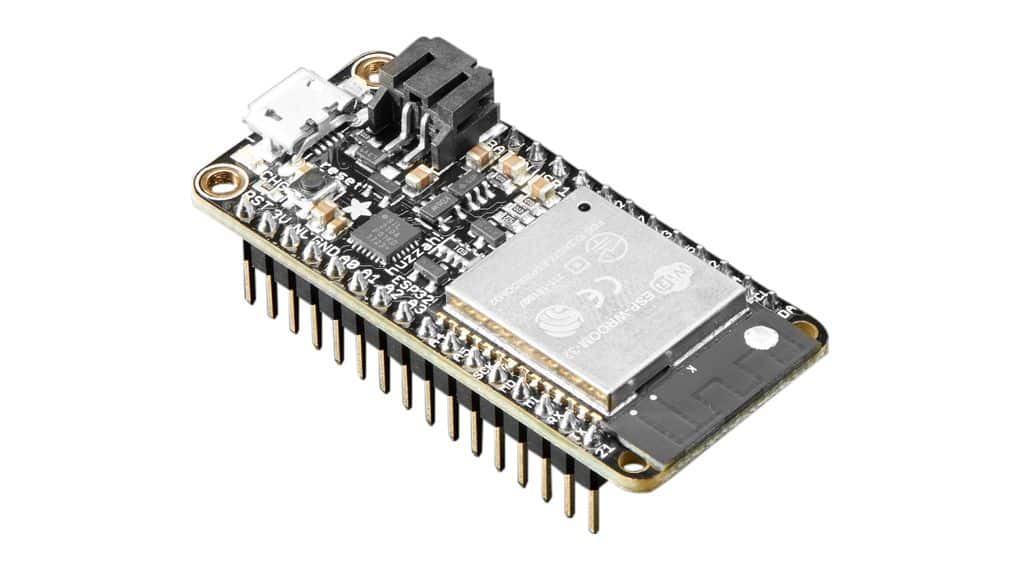

HUZZAH32
This development board is favored by beginners in IoT. It integrates the ESP32 with additional hardware, which makes it easier to program and use in projects.

Node-MCU-32S
The NodeMCU development board features Wi-Fi+Bluetooth connectivity, onboard CP2102 and keys.
A key feature of this AI Thinker development board is that the I/O pins of the ESP-WROOM-32 module are accessible via the extension headers. Moreover, it is open-source and supports several different source codes.
Final thoughts
No single article can cover all of the ESP32 series features. However, this information should provide a good starting point for you to find the best ESP32 chips, modules, and development boards for your IoT projects.
Read Our Other Resources
We’ve published a range of other IoT resources for our community, including:
- A remote control end-to-end example on ESP32: The Nabto ESP32 Virtual Thermostat Guide.
- A complete guide to Microcontrollers for IoT to help you choose the right MCU for your IoT project.
- How to Make a Low-Cost ESP32-Based Remote-Accessible Camera using ESP32-CAM or ESP32-EYE Board, which is a full tutorial for how to create an ESP32 camera with Nabto.