You’ve probably heard of smart buildings before, or possibly smart homes, but you may not know what makes a building “smart.” Smart buildings use internet-enabled devices to provide safety and comfort to occupants while monitoring and regulating various aspects of the building environment, such as energy efficiency and security.
These devices are part of what has come to be called the Internet of Things (IoT), which involves any number of physical electronic sensors and actuators that are connected to the internet and to each other. The devices are usually connected to some kind of app, which provides both management and occupants with a way of interacting with those devices. One very simple example would be a smartphone app that lets you control your smart TV.
Smart buildings have quickly become part of nearly every industry: more than 80% of businesses have experienced increased efficiency through IoT systems. What are some of the latest smart building IoT projects? And what can they do to make buildings and businesses more efficient?
Smart Building Trends
There are three primary types of smart buildings: smart homes, smart commercial buildings, and smart manufacturing facilities. And they each use IoT technology a little differently, depending on the usage and occupants of the buildings in question.
Smart homes could be anything from individual residences to apartment buildings to residential care facilities. Smart commercial buildings include office buildings, health-care facilities, and retail buildings. Both smart homes and smart commercial spaces can use IoT to create what’s called a BAS, or Building Automation Facility, in which owners and users can optimize indoor environments in terms of climate control, energy efficiency, site security, and more.
In addition to these functions, smart manufacturing also employs Operational Technology (OT), which means that IoT devices directly control various aspects of the manufacturing facility and its processes.
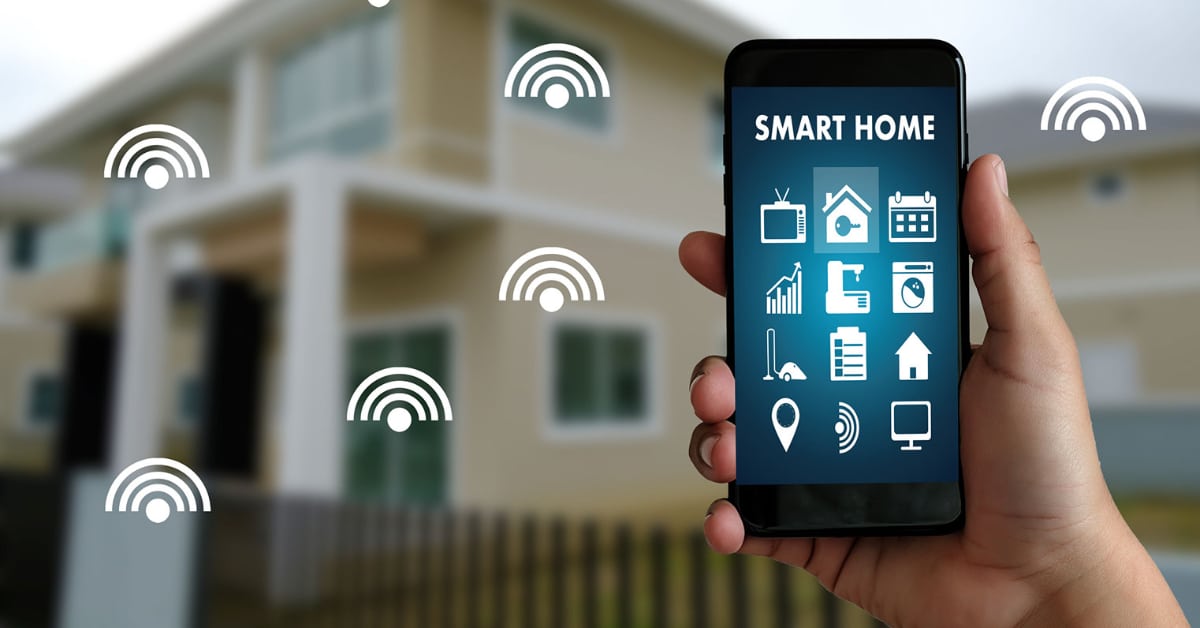
IoT Projects for Smart Homes
The global smart home market is expected to reach well over $100 billion this year. Residential buildings can use IoT to create a BAS that allows you to control things like air conditioning systems and security, all from, say, an app on your smartphone.
BAS systems work like this: IoT devices have built-in sensors that collect information about the building environment. Once you have the sensors in place collecting data, you need to process and transfer that information through a database, a server, or a fast P2P (Peer to Peer) system such as the one that Nabto provides.
Processing and analyzing the data will let you figure out, for example, the optimal indoor temperature to maintain both comfort and efficient energy consumption. Then actuators, which are IoT device components that perform a particular action, can adjust the temperature according to that data.
Besides optimizing the indoor environment, IoT systems can also control and monitor security systems. Security cameras that are part of an IoT system can provide real-time video surveillance to your computer or phone through a security monitoring app. That means you can monitor your home’s security on-site or remotely, even if you’re on vacation miles away from your house.

IoT for Commercial Smart Buildings
Trends for IoT applications in commercial buildings include systems for regulating and monitoring indoor air quality, energy usage, and, of course, security.
Smart lighting allows you to control lighting throughout a building based on information collected from IoT sensors. Buildings usually divide lighting into zones to optimize energy usage in each area based on current occupancy as well as ambient lighting from windows at different times of day. You can control the lighting manually from a computer or phone, or you can set your lighting system to optimize light levels automatically. Over time, IoT can save businesses up to 80% off their typical costs for lighting.
In these days when many businesses are looking to go green, IoT is one of the best ways to collect information about energy usage and reduce a company’s carbon footprint. Companies using IoT have been able to lower their energy consumption levels by as much as 40%.
Indoor air quality is a serious concern for employees in various commercial and manufacturing sectors. IoT sensors can collect information about air quality, including temperature and humidity levels. The sensors can even recognize harmful contaminants and alert employees and management of any danger.
When it comes to security, IoT systems can employ advanced facial recognition technology to ensure that no unauthorized personnel enter the building or a particular sector within the building.
IoT can also be applied outside of the office environment, for instance in an agricultural setting to gauge things like water usage or greenhouse temperatures. Agricultural businesses can also use internet-enabled robotics tools to perform simple farming tasks.
IoT in Manufacturing
Use cases for smart buildings in manufacturing often involve Operational Technology. Applications include controlling liquid and temperature levels, creating automated alerts, and practicing predictive maintenance.
Manufacturing uses different types of liquids, such as coolants and lubricants, to keep machines running smoothly. IoT technology allows manufacturers to monitor, increase, and decrease liquid levels as necessary and automatically.
Automated alerts start with sensors that detect issues that need attention from employees. For example, a sensor could detect a potentially dangerous chemical spill or unnaturally high temperatures in a machine that could lead to a fire. That data gets processed and transferred to some kind of hub or interface to let you know exactly what and where the problem is.
Predictive maintenance is a fast-growing practice for avoiding serious breakdowns in the manufacturing process. IoT sensors gather data showing where maintenance may soon be necessary and head off potential problems with automated maintenance tools. Predictive maintenance reduces production downtime and, thanks to IoT actuators, doesn’t usually require human intervention. One company reported that they were able to diagnose and solve 78% of issues without human intervention once they implemented predictive maintenance apps.
Predictive maintenance requires fast data transfer from sensors to actuators within an IoT network. Many businesses rely on cloud-based database technology to store and analyze data before it gets sent to its destination. The problem there is latency, or the delay in response time from the actuator because data needs to move through the database or server. With a P2P IoT platform, such as the one that we offer here at Nabto, the data goes straight from the sensors to the destination with no intermediary, which optimizes time-sensitive analysis and response.
Final Considerations
IoT projects for smart buildings require a lot of thought and planning, but more than nine out of ten CEOs believe that the benefits of IoT far outweigh any upfront effort or expense. Understanding the trends and benefits can help you optimize your projects to reduce energy usage and minimize maintenance costs. The smart building industry will only continue to grow in the coming years, with even more exciting and efficient possibilities on the horizon.
Read Our Other Resources:
- Six Ways IoT is Revolutionizing Agriculture, which gives more information about agricultural IoT trends
- Our guide to Low Latency In IoT – Why Is It Important? (And How to Achieve It)
- How to Develop IoT Apps. An Expert Guide by an IoT Developer, which tells you what you need to know to start developing your own smart building applications